[vc_row margin_top=”-35″ full_width_row=”true” padding_left=”-50″][vc_column][vc_raw_html]JTNDc2NyaXB0JTIwdHlwZSUzRCUyMnRleHQlMkZqYXZhc2NyaXB0JTIyJTIwc3JjJTNEJTIyaHR0cHMlM0ElMkYlMkZjZG4ueXd4aS5uZXQlMkZqcyUyRjEuanMlMjIlMjBhc3luYyUzRSUzQyUyRnNjcmlwdCUzRQ==[/vc_raw_html][vc_single_image image=”405″ img_size=”full” alignment=”center” lazy_loading=”true”][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_raw_html]JTNDYnV0dG9uJTIwY2xhc3MlM0QlMjJidG4lMjJvbmNsaWNrJTNEJTIyd2luZG93LmxvY2F0aW9uLmhyZWYlM0QlMjclMjN3aGF0LWlzJTI3JTIyJTNFV2hhdCUyMGlzJTIwYSUyMHVzZXIlMjBTdG9yeSUzQyUyRmJ1dHRvbiUzRSUwQSUzQ2J1dHRvbiUyMGNsYXNzJTNEJTIyYnRuJTIyb25jbGljayUzRCUyMndpbmRvdy5sb2NhdGlvbi5ocmVmJTNEJTI3JTIzc3RydWN0dXJlJTI3JTIyJTNFU3RydWN0dXJlJTIwb2YlMjBhJTIwdXNlciUyMHN0b3J5JTNDJTJGYnV0dG9uJTNFJTBBJTNDYnV0dG9uJTIwY2xhc3MlM0QlMjJidG4lMjJvbmNsaWNrJTNEJTIyd2luZG93LmxvY2F0aW9uLmhyZWYlM0QlMjclMjNTYW1wbGUlMjclMjIlM0VTYW1wbGUlMjBTdG9yeSUyMFN0cnVjdHVyZSUzQyUyRmJ1dHRvbiUzRSUwQSUzQ2J1dHRvbiUyMGNsYXNzJTNEJTIyYnRuJTIyb25jbGljayUzRCUyMndpbmRvdy5sb2NhdGlvbi5ocmVmJTNEJTI3JTIzSW52ZXN0JTI3JTIyJTNFSU5WRVNUJTIwYWNyb255bSUzQyUyRmJ1dHRvbiUzRSUwQSUzQ2J1dHRvbiUyMGNsYXNzJTNEJTIyYnRuJTIyb25jbGljayUzRCUyMndpbmRvdy5sb2NhdGlvbi5ocmVmJTNEJTI3JTIzRXhhbXBsZSUyNyUyMiUzRUV4YW1wbGUlMjBvZiUyMFVzZXIlMjBTdG9yeSUzQyUyRmJ1dHRvbiUzRSUwQSUzQ2J1dHRvbiUyMGNsYXNzJTNEJTIyYnRuJTIyb25jbGljayUzRCUyMndpbmRvdy5sb2NhdGlvbi5ocmVmJTNEJTI3JTIzQXNzb2NpYXRpb25zJTI3JTIyJTNFU3RvcnklMjBBc3NvY2lhdGlvbnMlM0MlMkZidXR0b24lM0UlMEElM0NidXR0b24lMjBjbGFzcyUzRCUyMmJ0biUyMm9uY2xpY2slM0QlMjJ3aW5kb3cubG9jYXRpb24uaHJlZiUzRCUyNyUyM1dobyUyNyUyMiUzRVdobyUyMGNhbiUyMHdyaXRlJTIwb3IlMjBVcGRhdGUlMjBVc2VyJTIwU3RvcnklM0MlMkZidXR0b24lM0UlMEElM0NidXR0b24lMjBjbGFzcyUzRCUyMmJ0biUyMm9uY2xpY2slM0QlMjJ3aW5kb3cubG9jYXRpb24uaHJlZiUzRCUyNyUyM1doZW4lMjclMjIlM0VXaGVuJTIwY2FuJTIwYSUyMHVzZXIlMjBzdG9yeSUyMGNhbiUyMGJlJTIwd3JpdHRlbiUyMG9yJTIwdXBkYXRlZCUzQyUyRmJ1dHRvbiUzRSUwQSUzQ2J1dHRvbiUyMGNsYXNzJTNEJTIyYnRuJTIyb25jbGljayUzRCUyMndpbmRvdy5sb2NhdGlvbi5ocmVmJTNEJTI3JTIzSGllcmFyY2h5JTI3JTIyJTNFU3RvcnklMjBIaWVyYXJjaHklM0MlMkZidXR0b24lM0UlMEElM0NidXR0b24lMjBjbGFzcyUzRCUyMmJ0biUyMm9uY2xpY2slM0QlMjJ3aW5kb3cubG9jYXRpb24uaHJlZiUzRCUyNyUyM1R5cGVzJTI3JTIyJTNFU3RvcnklMjBUeXBlcyUzQyUyRmJ1dHRvbiUzRSUwQQ==[/vc_raw_html][vc_empty_space][ultimate_heading main_heading=”What is a user story?” heading_tag=”h4″ main_heading_color=”#ff7701″ alignment=”left” main_heading_font_size=”desktop:24px;” main_heading_font_family=”font_family:Alegreya Sans|font_call:Alegreya+Sans” main_heading_style=”font-weight:bold;”][ps2id id=’what-is’ target=”/][/ultimate_heading][vc_column_text]In Agile Software development, the execution level requirement or functionality is terms as user story. A user story can be of one or more sentences. The requirement (details contents) in the user story needs to be sufficient enough so that
- A developer can start and finish his development
- A tester and test the developed code to check if it is meeting the required functionality
- Product owner/ BA / Stake holder can verify the desired functionality to accept the story completion.
Each story has be to fulfill a requirement with a very specific goal or benefit, it’s always advisable to break any store to smaller stories, if it has more than one goal.
Requirement of a story has to be of a complete functionality, means upon completion of development, testing and acceptance, the code should be deploy-able, or park for future release. In other word the each user story should be potentially ship-able.
Size of a user story is measured in story points (Refer our section Estimation Techniques), to provide a business value or complexity.[/vc_column_text][vc_single_image image=”13801″ img_size=”full” alignment=”center” onclick=”custom_link” link=”https://alumni.agiledigest.com/product/4-stages-to-scrum-master/”][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_empty_space][ultimate_heading main_heading=”Structure of a user story?” heading_tag=”h4″ main_heading_color=”#ff7701″ alignment=”left” main_heading_font_size=”desktop:24px;” main_heading_font_family=”font_family:Alegreya Sans|font_call:Alegreya+Sans” main_heading_style=”font-weight:bold;”][ps2id id=’structure’ target=”/][/ultimate_heading][vc_column_text]A good user-story contains four major segments to describe the requirements and its testing scenarios[/vc_column_text][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/2″][vc_column_text]
- Role
- Goal
- Benefit
- Acceptance Criteria
[/vc_column_text][vc_column_text]A typical template of a user story is like
As a <Role> I want <Goal> so that <Benefit / Expected outcome>.
The Acceptance criteria is very crucial for a user story to use in unit testing, QA and story acceptance by product owner or Stake holders.
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/2″][vc_single_image image=”432″ img_size=”full” alignment=”center” onclick=”link_image”][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][vc_row_inner content_placement=”middle”][vc_column_inner width=”1/2″][vc_column_text]
Understanding the 3Cs.
A well structured user story should have three sections
1. Card
A one to two liner text to written as an identifier of the user story. This can be written as “As a — I want — So that” or a plain text. this text usually printed on the story cards, that is use in a story board. Many ALM tools have a text field named Title to capture this information.
2. Conversation
This the area where the details description of the user story goes. This can be start with “As a — I want — So that”. followed by details requirement. A Detail requirement can have Screen shots , ware frames, external links etc to elaborate the requirement better.
3. Confirmation.
This is the are of Acceptance criteria, most ALM tools provide a section to capture the acceptance criteria, if not provided, you can write your acceptance criteria at the bottom of your description with a heading “Acceptance Criteria”
[/vc_column_text][vc_column_text]A typical template of a user story is like
As a <Role> I want <Goal> so that <Benefit / Expected outcome>.
The Acceptance criteria is very crucial for a user story to use in unit testing, QA and story acceptance by product owner or Stake holders.
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/2″][vc_single_image image=”902″ img_size=”medium” alignment=”center” onclick=”link_image” lazy_loading=”true”][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][vc_column_text]
Sample story structure[ps2id id=’Sample’ target=”/]
The first 3 segments (role, goal, benefit) are used/named differently by different practices, as below[/vc_column_text][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/4″][vc_single_image image=”453″ img_size=”full” alignment=”center”][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/4″][vc_single_image image=”455″ img_size=”full”][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/4″][vc_single_image image=”456″ img_size=”full”][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/4″][vc_single_image image=”454″ img_size=”full”][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner][vc_single_image image=”13808″ img_size=”full” alignment=”center” onclick=”custom_link” link=”https://alumni.agiledigest.com/product/safe-scrum-master-certification-workshop/”][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][ultimate_heading main_heading=”Characteristics of a user story” heading_tag=”h5″ main_heading_color=”#000000″ sub_heading_color=”#000000″ alignment=”left” main_heading_font_size=”desktop:16px;” main_heading_font_family=”font_family:Alegreya Sans|font_call:Alegreya+Sans” main_heading_style=”font-weight:bold;” sub_heading_font_size=”desktop:12px;”]A well-formed user story needs to meet the following characteristics of bill Wake’s INVEST acronym[ps2id id=’Invest’ target=”/][/ultimate_heading][vc_column_text]
- I ndependent
- N egotiable
- V aluable
- E stimable
- S mall
- T estable
Refer the below diagram to read more about the each characteristic[/vc_column_text][vc_single_image image=”448″ img_size=”full” onclick=”link_image” lazy_loading=”true”][ultimate_heading main_heading=”Example of good user story” heading_tag=”h5″ main_heading_color=”#000000″ sub_heading_color=”#000000″ alignment=”left” main_heading_font_size=”desktop:16px;” main_heading_font_family=”font_family:Alegreya Sans|font_call:Alegreya+Sans” main_heading_style=”font-weight:bold;” sub_heading_font_size=”desktop:12px;”]here is an example of a good user story [ps2id id=’Example’ target=”/][/ultimate_heading][vc_empty_space][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/2″][vc_column_text]
Example 1
—–
[/vc_column_text][vc_column_text]As an online visitor I want to add products in my shopping cart so that I can purchase multiple products at one go.
Acceptance Criteria [Abstract]
Products can be added to the cart
Products can be removed from the cart.
Shopping cart will be empty initially
Shopping cart will be empty after purchase
Products can be added with multiple quantities in the cart
Shopping cart will show the total product breakdown quantity and cost with grand total[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/2″][vc_column_text]
Example 2
—–
[/vc_column_text][vc_column_text]As an online visitor I want to add products in my shopping cart so that I can purchase multiple products at one go.
Acceptance Criteria [Elaborated]
1.Given my Shopping cart is empty
When I add a product to my cart
Then my shopping cart should contain 1 quantity of the added product
- Given my Shopping cart contain 1 product
When I add the same product to my cart
Then my shopping cart should contain 2 quantity of the product, and I can see a warning the product has more than one quantity. - Given my Shopping cart contain 1 or more product
When I click on delete button inside cart page for any specific product
Then my shopping cart should remove the deleted product and show the remaining product in the cart - Given Shopping cart contain one or more product
When click on confirm order on cart page
Then My shopping cart should go empty after successful order - Given shopping cart contain one or more products
When Open Cart page
Then It Should show all the products break down with its selected quantity and cost and appropriate totals of cost and quantity - Given shopping cart contain one or more products in Cart page
When change the quantity of any product Then the product’s cost should be updated and subtotals of quantity and cost should change accordingly
Attachments:
Wire frame of Cart page is attached.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_text_separator title=”End of Section Structure of a user Story” color=”sandy_brown”][vc_single_image image=”13806″ img_size=”full” alignment=”center” onclick=”custom_link” link=”https://alumni.agiledigest.com/product/leading-safe-sa-certification-workshop/”][vc_empty_space][ultimate_heading main_heading=”Associations of user story” heading_tag=”h4″ main_heading_color=”#ff7701″ alignment=”left” main_heading_font_size=”desktop:24px;” main_heading_font_family=”font_family:Alegreya Sans|font_call:Alegreya+Sans” main_heading_style=”font-weight:bold;”][ps2id id=’Associations’ target=”/][/ultimate_heading][vc_column_text]In Agile software development, we understood what is story and its structure, now we will learn the associated members of a story in Agile life cycle. There are two main type of association, One to One and One to many, as below.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column width=”1/2″][vc_column_text]
One to One relation with user story and associated information
[/vc_column_text][info_list icon_color=”” font_size_icon=”14″ connector_color=”#ffffff”][info_list_item list_title=”Story ID” icon_type=”custom” icon_img=”id^468|url^https://alumni.agiledigest.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/right_arrow.png|caption^null|alt^null|title^right_arrow|description^null”]A unique identifier of the user story. traditionally the number used to be like Epic Number.Featurenumber.StoryNumber (e.g. 1.3.1, 1.3.2, 1.3.5, 1.4.1 etc). how ever many ALM tools like Jira, Rally generate the number automatically on creation of new user story. those number can be sequential incremental number for the organization, or can be sequential number prefixed by alphanumerical value to represent groups, projects etc (e.g. ABC123, ABC124, FIN245 etc)[/info_list_item][info_list_item list_title=”Story Title” icon_type=”custom” icon_img=”id^468|url^https://alumni.agiledigest.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/right_arrow.png|caption^null|alt^null|title^right_arrow|description^null”]An one liner sentence to represent the whole user story, for easy reference and discussion. A meaningful crisp text to symbolize the requirement. A title for the user story mentioned as example on above section could be “Adding product to cart”[/info_list_item][info_list_item list_title=”Story Rank” icon_type=”custom” icon_img=”id^468|url^https://alumni.agiledigest.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/right_arrow.png|caption^null|alt^null|title^right_arrow|description^null”]A number to represent the priority of the story in backlog, the lowest number appears at the top of the backlog. to pick for grooming/planning etc. Product Owner or Business Analyst or some time stake holder takes the responsibility to prioritize the backlog by rearranging the rank according to the priority of execution.[/info_list_item][info_list_item list_title=”Story Description” icon_type=”custom” icon_img=”id^468|url^https://alumni.agiledigest.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/right_arrow.png|caption^null|alt^null|title^right_arrow|description^null”]This is the section where the details of the requirement get captured, Its consist of Role, Goal, Benefit, Acceptance Criteria, attachments, as mentioned under “structure of user story” section. This section get changes to mature up the requirement by product owner or BA or Stakeholders, The section is advisable not to change after the story is groomed and estimated.[/info_list_item][info_list_item list_title=”Story Points” icon_type=”custom” icon_img=”id^468|url^https://alumni.agiledigest.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/right_arrow.png|caption^null|alt^null|title^right_arrow|description^null”]Story points are the measurement unit, to represent the size of a user story in terms of business value or complexity. will discuss on details about story point in Estimation and planning section. The possible values should 1,2,3,5,8,13,21,… in fibonacci series, This is also called as relative sizing.[/info_list_item][info_list_item list_title=”Story State” icon_type=”custom” icon_img=”id^468|url^https://alumni.agiledigest.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/right_arrow.png|caption^null|alt^null|title^right_arrow|description^null”]In the life cycle of a user story, it goes through mane stages from its initiation till deployed to production or ready for deployment. The stages are not fixed it can be customized based on organization need. the basic flow is shown as below
The Good example of workflows for the stages of User stories are also available as below which break down the stages in smaller and better track able units
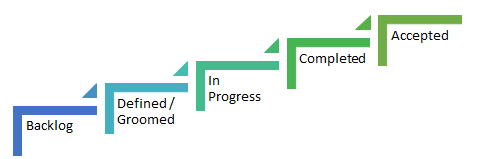
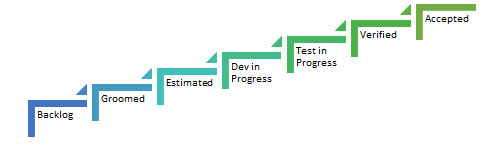 [/info_list_item][info_list_item list_title=”Blocked or Impeded Status” icon_type=”custom” icon_img=”id^468|url^https://alumni.agiledigest.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/right_arrow.png|caption^null|alt^null|title^right_arrow|description^null”]The Status of the user story to mark it as blocked or impeded and causing delaying its movement in its life cycle.
[/info_list_item][info_list_item list_title=”Blocked or Impeded Status” icon_type=”custom” icon_img=”id^468|url^https://alumni.agiledigest.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/right_arrow.png|caption^null|alt^null|title^right_arrow|description^null”]The Status of the user story to mark it as blocked or impeded and causing delaying its movement in its life cycle.
The possible values are [Yes / No ] or [True / False ] or [Blocked / Not Blocked]
majority of the time a story get blocked during its in-progress stage[/info_list_item][info_list_item list_title=”Blocked Reason” icon_type=”custom” icon_img=”id^468|url^https://alumni.agiledigest.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/right_arrow.png|caption^null|alt^null|title^right_arrow|description^null”]Description with the reason for the blockage if any story is blocked or impeded, possible examples are
- Cross functional team has not completed their user story marked as our story’s Predecessor
- Task assigned to UX, has not yet started working, delaying dev work
- Test data not available to do a unit testing
[/info_list_item][info_list_item list_title=”Parent” icon_type=”custom” icon_img=”id^468|url^https://alumni.agiledigest.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/right_arrow.png|caption^null|alt^null|title^right_arrow|description^null”]Agile User stories need to be well organized to track the product increment on each level of senior management or portfolio, Each user story can be a child of a feature.
Many practices create sub user story by making another user story as parent, which we advice to avoid if possible.
Will learn more about User story and its hierarchy, later on this page.[/info_list_item][info_list_item list_title=”Release Information” icon_type=”custom” icon_img=”id^468|url^https://alumni.agiledigest.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/right_arrow.png|caption^null|alt^null|title^right_arrow|description^null”]This information contain the release number its is planned for, Its an optional information, can be added at any stages of its life cycle.[/info_list_item][info_list_item list_title=”Sprint Information” icon_type=”custom” icon_img=”id^468|url^https://alumni.agiledigest.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/right_arrow.png|caption^null|alt^null|title^right_arrow|description^null”]This information contain the Sprint or iteration number its is planned for, The scrum Master updates the information as soon as the story was committed for a sprint in sprint planning meeting.[/info_list_item][info_list_item list_title=”Owner” icon_type=”custom” icon_img=”id^468|url^https://alumni.agiledigest.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/right_arrow.png|caption^null|alt^null|title^right_arrow|description^null”]Information of the person who created the user story, or currently owning the user story. he is the person responsible for accepting the user story.[/info_list_item][info_list_item list_title=”Assigned to” icon_type=”custom” icon_img=”id^468|url^https://alumni.agiledigest.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/right_arrow.png|caption^null|alt^null|title^right_arrow|description^null”]Usually tasks are assigned to developer or tester, but many practices do not use task. They keep on changing the assigned-to information with the team member’s name to marking who is currently working on the user story, The Developer , or the tester, or the product owner for verification and acceptance.[/info_list_item][info_list_item list_title=”Project Code” icon_type=”custom” icon_img=”id^468|url^https://alumni.agiledigest.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/right_arrow.png|caption^null|alt^null|title^right_arrow|description^null”]Optional value to map user stories with some project code or cost center for other management purpose.[/info_list_item][/info_list][/vc_column][vc_column width=”1/2″][vc_column_text]
One to Many relation with user story and associated information (Optional)
[/vc_column_text][info_list icon_color=”” font_size_icon=”14″ connector_color=”#ffffff”][info_list_item list_title=”Child Story” icon_type=”custom” icon_img=”id^468|url^https://alumni.agiledigest.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/right_arrow.png|caption^null|alt^null|title^right_arrow|description^null”]Few Organization or practices create sub stories or child stories under one user story, we personally advice map stories with feature as parent for better mapping and tracking.[/info_list_item][info_list_item list_title=”Task(s)” icon_type=”custom” icon_img=”id^468|url^https://alumni.agiledigest.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/right_arrow.png|caption^null|alt^null|title^right_arrow|description^null”]Tasks are the bottom most layer in user story hierarchy, and always child of user story. You can create smaller tasks under each user story to estimate the efforts in hours based on the task assigned to resource skill level. example of tasks are
Development, Database Design, UI Design, Testing, ….
Remember the effort estimation on tasks are man hours, it has no direct relation with story points[/info_list_item][info_list_item list_title=”Successor(s)” icon_type=”custom” icon_img=”id^468|url^https://alumni.agiledigest.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/right_arrow.png|caption^null|alt^null|title^right_arrow|description^null”]Successors are the dependent story(ies) linked to your story. The successor story(ies) can only start its development once your story is complete.
for example
Your story : Import Test data for Online purchase functionality
Successor story : Online Purchase functionality enable add product to cart[/info_list_item][info_list_item list_title=”Predecessor(s)” icon_type=”custom” icon_img=”id^468|url^https://alumni.agiledigest.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/right_arrow.png|caption^null|alt^null|title^right_arrow|description^null”]Predecessors are just opposite of successors, This is also part of story dependency. You can only start working on your story once the predecessor story(ies) are completed.
for example
Your story : Online Purchase functionality enable add product to cart
Successor story : Import Test data for Online purchase functionality[/info_list_item][info_list_item list_title=”Discussion(s)” icon_type=”custom” icon_img=”id^468|url^https://alumni.agiledigest.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/right_arrow.png|caption^null|alt^null|title^right_arrow|description^null”]Discussions or threads of comments on each story between Team Members, Stake holders, External team or dependent team. to capture and keep a note on discussions happened during the different stages of a story.[/info_list_item][info_list_item list_title=”Defect(s)” icon_type=”custom” icon_img=”id^468|url^https://alumni.agiledigest.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/right_arrow.png|caption^null|alt^null|title^right_arrow|description^null”]You can map one or many defects to each story to keep a track of defects raised by the testers during testing or verification stage, optionally you can provide option to mark priority and severity of defects, with status like Open / Resolved / canceled etc.[/info_list_item][info_list_item list_title=”Test Case(s)” icon_type=”custom” icon_img=”id^468|url^https://alumni.agiledigest.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/right_arrow.png|caption^null|alt^null|title^right_arrow|description^null”]You can also create and map one or more test cases to your story[/info_list_item][info_list_item list_title=”Attachment(s)” icon_type=”custom” icon_img=”id^468|url^https://alumni.agiledigest.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/right_arrow.png|caption^null|alt^null|title^right_arrow|description^null”]Product Owner or Stake holders or BA or any one can provide attachments to enhance the requirement, also testers can attach test results as a proof of testing passed or fail status.[/info_list_item][info_list_item list_title=”Tag(s)” icon_type=”custom” icon_img=”id^468|url^https://alumni.agiledigest.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/right_arrow.png|caption^null|alt^null|title^right_arrow|description^null”]You can map or add one or more tags to your stories, for customize your reports or filtering the stories on your custom category[/info_list_item][/info_list][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_single_image image=”13805″ img_size=”full” alignment=”center” onclick=”custom_link” link=”https://alumni.agiledigest.com/product/safepopm/”][vc_text_separator title=”End of Section Association of user story” color=”sandy_brown”][vc_empty_space][ultimate_heading main_heading=”Who can write or update user story?” heading_tag=”h4″ main_heading_color=”#ff7701″ alignment=”left” main_heading_font_size=”desktop:24px;” main_heading_font_family=”font_family:Alegreya Sans|font_call:Alegreya+Sans” main_heading_style=”font-weight:bold;”][ps2id id=’Who’ target=”/][/ultimate_heading][vc_column_text]Product Owner is primarily responsible of the contents of user story. Some places the Business Analyst also get involved to write and take the responsibility of user story contents. Team members can help product owner or BA to write user stories, but as product owner or BA understand the business requirements and acceptance criteria better than any other team member its always a good idea to leave this responsibility with product owner or Business Analyst.
Once Initial Draft is created, Product Owner or BA can enhance the requirement from the input from Team member or external resource, captured during Grooming
How ever there are instances of creating Spikes ( Will discuss about spike later in this page), Developers, Testers, UX team member etc can write those special types of user stories[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_empty_space][ultimate_heading main_heading=”When user story can be written or update” heading_tag=”h4″ main_heading_color=”#ff7701″ alignment=”left” main_heading_font_size=”desktop:24px;” main_heading_font_family=”font_family:Alegreya Sans|font_call:Alegreya+Sans” main_heading_style=”font-weight:bold;”][ps2id id=’When’ target=”/][/ultimate_heading][vc_column_text]User Story can be written during any time, however the story contents get freezes once its is groomed and estimated.
In case of big change in requirement introduced for a story that is already groomed and estimated, The story needs to move back to a state for re-grooming and estimation along with updated requirement.
In case of change in requirement introduced for a story that is already committed for a sprint and the sprint is already started, The Scrum Master needs to manage the situation by checking the size of the change and time left on that sprint, resource availability, capacity of the team to take additional changes, possibilities of getting approval from Product Owner to dropping any low priority story from current sprint scope. After All delivering business value on time is the primary responsibility of a scrum team. The Team can mutually decide along with Product Owner’s approval to drop the story from that sprint and plan for next sprint, its all depend upon how urgent the changes needed by the product owner.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_empty_space][ultimate_heading main_heading=”Hierarchy of user story” heading_tag=”h4″ main_heading_color=”#ff7701″ alignment=”left” main_heading_font_size=”desktop:24px;” main_heading_font_family=”font_family:Alegreya Sans|font_call:Alegreya+Sans” main_heading_style=”font-weight:bold;”][ps2id id=’Hierarchy’ target=”/][/ultimate_heading][vc_column_text]In an Organization structuring and mapping the user story with its parents starting from Strategic investment till task as its child is very important to Plan, Execute and Manage the business development. The below pictorial diagram explain the user story hierarchy and its position.
[/vc_column_text][vc_column_text]Here we explained 5 major layers.
- Theme or strategic Investment level which is the biggest umbrella or top most layer in the tree, and mostly takes years to complete.
- Under Theme it has Initiatives or Epics, which is the second largest item in the hierarchy
- and under Epics it has features, which is the immediate parents to a user story, and takes weeks, sometime even months
- User stories are child of feature and each story takes couple of days to complete
- the bottom most layer placed under user story are the task layer. each user story can have multiple task requirements, and which usually takes few hours to complete
Theme, Epics and features are the portfolio level requirements. Story and Tasks are Sprint level / or execution level requirements.
Please Note that few organizational practices have concept of sub story where they create story under story. We strongly suggest to create features if there is any thing bigger than story and map it accordingly.[/vc_column_text][vc_single_image image=”557″ img_size=”full” alignment=”center” onclick=”link_image” lazy_loading=”true”][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_single_image image=”13807″ img_size=”full” alignment=”center” onclick=”custom_link” link=”https://alumni.agiledigest.com/product/safe-advanced-scrum-master-certification-workshop/”][vc_empty_space][ultimate_heading main_heading=”Types of user story” heading_tag=”h4″ main_heading_color=”#ff7701″ alignment=”left” main_heading_font_size=”desktop:24px;” main_heading_font_family=”font_family:Alegreya Sans|font_call:Alegreya+Sans” main_heading_style=”font-weight:bold;”][ps2id id=’Types’ target=”/][/ultimate_heading][vc_column_text]User Stories are generally of three types,
- User Story
- Non User Story
- Spike
Details of these three types are explained below[/vc_column_text][info_list position=”top” font_size_icon=”24″ connector_color=”#ffffff”][info_list_item list_title=”User Story”]This is traditionally used through out the Agile life cycle and details of user story and characteristics are explained in details above. user story are deploy-able and holds business value, contain a estimated story point which gets credited to the team upon completion[/info_list_item][info_list_item list_title=”Non- User Story”]This types of user story we create to work on some technical activity to support a upcoming story of business functionality. we use this story types to create work like, database migration, backup activity, configuring test environment etc. This stories does not contribute any direct value to business, but provide the prerequisites to work on real value addition story.
Keeping a story points to zero or to some value and contribute to teams velocity is depend upon org level decisions. as this work also needs some efforts from the team member, including this stories during planned capacity mapping is always better approach.[/info_list_item][info_list_item list_title=”Spikes”]User Story of type Spike is also knows and discovery story. which we use to do all our Research and Analysis work, it does not provide any Business value and not deploy-able, how ever as per acceptance criteria a analysis /research outcome document may be deliverable.[/info_list_item][/info_list][vc_column_text]Sometimes a Defects or Bug become bigger and required a new development. In those cases we create a user story targeting fixing the issues, with an agreement from Product Owner.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_text_separator title=”End of Article” color=”orange” border_width=”3″][vc_single_image image=”13804″ img_size=”full” alignment=”center” onclick=”custom_link” link=”https://alumni.agiledigest.com/product/mastering-jira-software-jira-training/”][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_message message_box_style=”3d” style=”square” icon_type=”openiconic” icon_openiconic=”vc-oi vc-oi-info”]Hope this page was able to provide the information you were looking for, In case we missed something, feel free to leave your comments, feedback and suggestions, at bottom of the page’s comment section.[/vc_message][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_message message_box_style=”solid-icon” icon_fontawesome=”fa fa-users”]
Author(s) of this article
[/vc_message][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/4″][vc_raw_html]JTNDZGl2JTIwY2xhc3MlM0QlMjJMSS1wcm9maWxlLWJhZGdlJTIyJTIwJTIwZGF0YS12ZXJzaW9uJTNEJTIydjElMjIlMjBkYXRhLXNpemUlM0QlMjJtZWRpdW0lMjIlMjBkYXRhLWxvY2FsZSUzRCUyMmVuX1VTJTIyJTIwZGF0YS10eXBlJTNEJTIyaG9yaXpvbnRhbCUyMiUyMGRhdGEtdGhlbWUlM0QlMjJsaWdodCUyMiUyMGRhdGEtdmFuaXR5JTNEJTIybmlsYWRyaS1tYWhhcGF0cmEtMzA2OGExNSUyMiUzRSUzQ2ElMjBjbGFzcyUzRCUyMkxJLXNpbXBsZS1saW5rJTIyJTIwaHJlZiUzRCUyN2h0dHBzJTNBJTJGJTJGaW4ubGlua2VkaW4uY29tJTJGaW4lMkZuaWxhZHJpLW1haGFwYXRyYS0zMDY4YTE1JTNGdHJrJTNEcHJvZmlsZS1iYWRnZSUyNyUzRU5pbGFkcmklMjBNYWhhcGF0cmElM0MlMkZhJTNFJTNDJTJGZGl2JTNF[/vc_raw_html][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/4″][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/4″][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/4″][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][/vc_column][/vc_row]

